A McKinsey survey of business leaders found that responses to COVID-19 have “speed the adoption of digital technologies by several years—and that many of these changes could be here for the long haul.” Digital adoption has taken a quantum leap at both the organizational and industry levels.
The change has impacted the workforce, and companies are struggling to adopt new ways to work. “The pandemic has confirmed what many already knew,” analysts at Gartner wrote. “Legacy ways of working are outdated.” Technology in the workplace is changing faster than companies can implement it. “COVID-19 has escalated digital initiatives into digital imperatives, creating urgent pressure on HR leaders to work with their CEO, CFO, and CIO to rethink skills needs as business models change at light speed,” Gartner said.
Only 30 percent of businesses succeed in implementing new technology at work. A major reason for failure is insufficient planning. You can’t just expect employees to take on the challenge of integrating a new tool into their workflow; you first have to provide proper training and support. Luckily, doing so is much easier than you think.
Here are five strategies to help you successfully implement new technology in your workplace:
- Include Employees in Technology in the Workplace Decisions
- Use Technology in the Workplace to Address Employee Pain Points
- Implement Technology in the Workplace Based on the Natural Diffusion of Innovation
- Leverage Workplace Technology Vendors
- Use Your Workplace Technology Training Tools
- Invest in a Technology in the Workplace Learning Platform
Let's dive in.
6 Steps for Implementing New Technology
1. Include Employees in the Implementation Process
Introducing new technology into the workplace impacts employee workflows and morale. When done right, new technology implementation can improve efficiency, cut costs, and help your team focus better on the work they do best. When done poorly, it can hurt morale, cause errors, and reduce efficiency.
That's why it's so important to consider employee feedback. Although the decision to buy new software might be final, involving employees in choosing the specific solution can make a big difference in adoption and impact. This feedback-first method applies to all tech tools, including communication platforms, video conferencing solutions, and CRM systems.
Implementation can look like this:
- Put out RFPs if necessary and narrow your options down to your top two or three choices.
- Provide a demo or test access to your team, highlighting the benefits of each option.
- Invite them to share their feedback, past experiences, and thoughts.
- Utilize this feedback in your decision-making process.
- Once you've selected a tool, highlight the impact their feedback had on your decision.
- If you move forward with a tool employees didn't prefer, take the time to clearly explain why, the constraints, and thank them for sharing their insights. It's important to make it clear that you took their feedback seriously.
The employees who preferred your selected tool will become internal advocates for adoption. If you effectively address the feedback from those who chose a competitor, these employees will feel heard. The goal is to make your team feel like they were part of the selection and technology implementation process.
Surveys find that employees who are involved in decision-making processes are more motivated, satisfied, and engaged in their jobs. Giving them a say in the outcome transforms technology adoption from a disturbance imposed on them into a collaborative effort to make the company more successful.
2. Explain How the Technology You're Implementing Addresses Employee Pain
The way you describe technology at work significantly influences employee attitudes. While you might have numerous metrics-based reasons for the purchase, these alone won't motivate your employees.
Employees make decisions with the same part of their brain that controls emotions, so to convince your employees to embrace a new tool, you need to excite them by explaining how it solves their pain points. You aren't just building a tech stack because you have to. You're intentionally selecting technology to address specific needs and make your team's lives easier.
In other words, what is in it for them?
For example, if you are implementing a more advanced CRM and one of your sales team’s main challenges is predicting which prospects and campaigns are most likely to generate sales, then explain how the new CRM has analytics tools that will help them obtain more qualified leads and close more deals.
If you are implementing software across multiple functional teams, change your message to reflect the specific benefits for each group. For example, if your finance team also must adopt the same new CRM, explain how it will enable them to make more accurate forecasts.
3. Implement Technology Based on the Natural Diffusion of Innovation
Humans naturally resist change; however, the extent to which we do so varies. The Diffusion of Innovation curve explains that people’s willingness to adopt innovative technology follows a bell curve divided into five groups, as shown below.
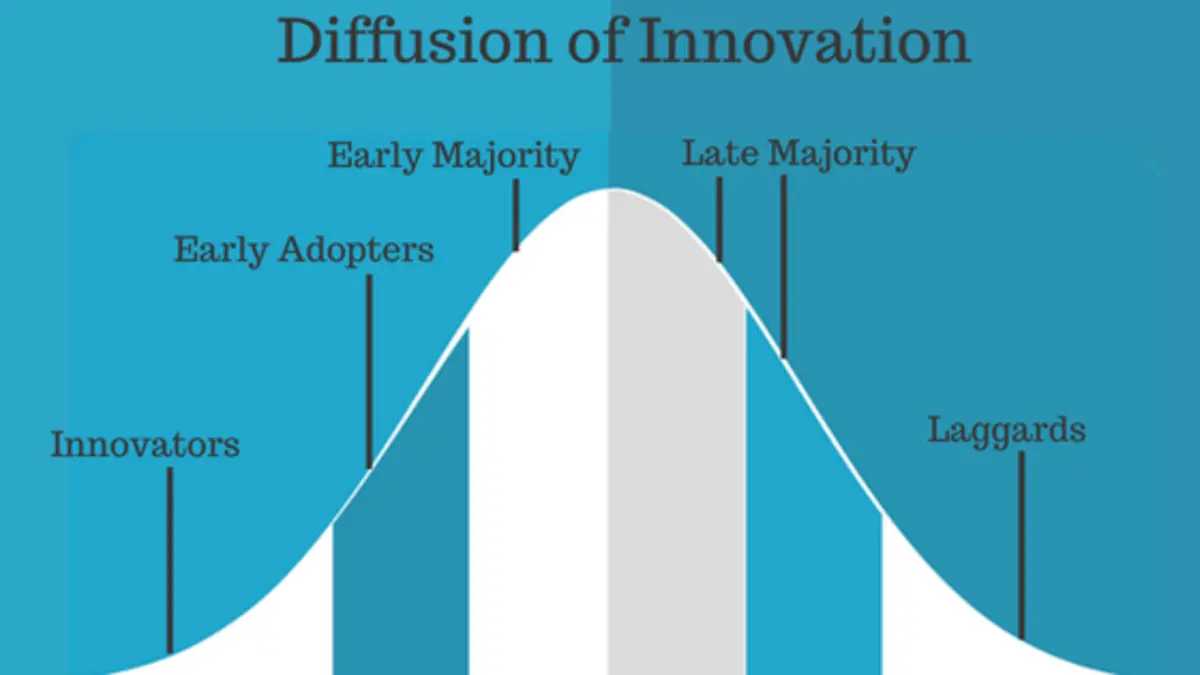
The percentage of your employees that fall into each of these groups may vary from the normal curve since your organization might attract people who are open to change. However, you certainly have employees in all categories. Understanding your team's different perspectives on innovation helps you plan a smoother implementation strategy.
Here are the five perspectives on new technology:
- Innovators: These employees are always asking for innovative technology and proposing new ways to complete work. Give them access to the software first so they can learn how to use it and teach other employees about it.
- Early Adopters: Early adopters' curiosity is piqued when they see the innovators using something new. They are the employees who show interest in your new systems but are not as eager or change-driving as innovators. Try forming a 1-2 week-long focus group with these individuals. Their questions, challenges, and feedback can help improve how you roll out the new system to the entire team.
- Early Majority: You will reach the early and late majority when you roll out the workplace technology to everyone. People in the early majority will quickly jump on board and work collaboratively to develop best practices.
- Late Majority: These are the grandparents on Facebook. People in this category will resist the implementation until they see proof that it works. They will have a lot of questions and some complaints early on. However, once they start realizing performance improvements, they will embrace the change.
- Laggards: These individuals will resist adopting new technology until you start punishing them for not using it. If possible, wait to force them to use it until you’ve worked through most of the errors, as they tend to be vocal complainers when they encounter issues.
Designing your implementation plan to cater to each of these groups will reduce the number of conflicts and resistance you face.
4. Leverage Your Workplace Technology Vendor
Most SaaS and other technology companies assign you a customer success manager. Leverage their technical expertise; they can accelerate your adoption by helping you navigate the learning curve. Customer success managers have assisted hundreds of companies with similar goals. Trust in their support.
Here are some questions you should ask your account manager:
- What are the best practices for using this software?
- Do you have any tips to make it easier to train my team?
- How do I do <most frequently asked question here?
- Are there any shortcuts that can help my team find information/produce reports/generate insights, etc., faster?
- Can I share your email with my team so they can reach out to you with questions?
Ask as many questions as you need to feel 100 percent confident using the tool.
Some workplace technology providers also offer onboarding programs to help teams become trained and comfortable using new tools in their work contexts. Usually, onboarding comes with a price (try to get it included for free), but it can be well worth it as a fast-track to productivity.
5. Use Your Workplace Technology Training Tools
If teaching your employees how to use new software is daunting, chances are you do not have to do it yourself. Many SaaS and other technology providers, such as Salesforce, HubSpot, and Microsoft, offer free training programs that guide users through every aspect of their software. Identify which sections are most useful to each of your employee groups and have your employees complete the relevant sections.
Though the training materials are excellent at explaining how to use the system, their assessments, if any, are often insufficient to demonstrate employee understanding. To ensure your team is learning the necessary skills, sync with them mid-training to check their progress. After they complete it, give them an assignment that tests their ability to use it. For example, you might ask them to input data and run a few reports, use the analytics to generate actionable insights, or create a workflow to automate a process.
6. Invest in a Workplace Technology Learning Platform
The reality is that technology in the workplace will continue to change rapidly. The so-called “shelf life” of employee skills is down to about two years. That means that the skills your employees possess today will become outdated in as little as two years. Someone who stopped using a platform like Salesforce two years ago will be far behind the learning curve if they start using it again now.
The World Economic Forum estimates that 85 million jobs will be lost to automation by 2025, and 97 million jobs requiring skills that do not yet exist will be created. The only way that businesses will be able to bridge this “skills gap” is with on-the-job skill-building.
Learning platforms like LinkedIn Learning enable your employees to continue to learn on the job. But you must use these platforms intentionally. You will need a structured approach. Structured learning is different from adopting a learning management system that employees can use at their discretion. Structured learning programs assess a company's current and required skills, generating individualized and group learning "journeys" for employees and teams aligned with business needs and goals. Every employee has a roadmap for continuing to learn the skills they will need. Structured learning solutions like Learn In build roadmaps for businesses and measure progress and impacts.
Technology in the Workplace Improves Productivity
It is well known that workplace technology can greatly boost your employees' productivity and your business's profitability. The pandemic has made this even clearer.
“Companies that were poised for digital transformation before COVID-19 are quickly distancing themselves from analog companies, and the rest are scrambling to catch up,” Gartner said. More and more roles are requiring technical skills, and businesses are racing to keep up. Focusing on successful workplace technology implementation can help them get farther, faster.
Still Struggling to Drive Technology Adoption?
Virtual assistants can handle the tedious work of keeping your systems updated, allowing you to leverage predictive insights without burdening your team. Want to learn more about working with VAs? Read our free guide.
